

|
|
|
|
CONTACT
FLOOD HISTORY
PHOTO GALLERY
SYSTEM COMPONENTS :
FORECASTS:
PROJECT
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
OPERATIONS
FORECASTS
|
CONCRETE FLOOD WALL
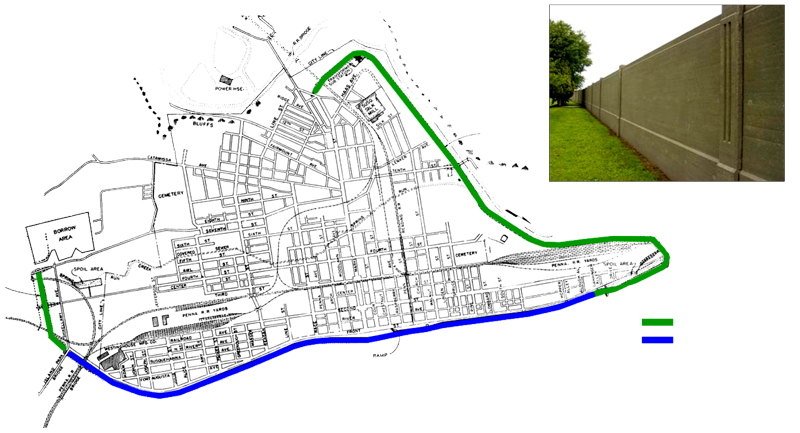
 Floodwall is constructed where clearance would be too restricted for levee construction. The floodwall is constructed of reinforced concrete with a steel sheet pile cutoff. There are two specific types of concrete floodwall, I-Wall and T-Wall. Each type has several different designs to accommodate different conditions. Concrete floodwall is constructed on-top “sheet pilings” (pictured at left). T-Wall sheet piling was driven through the soil down to bedrock. The “T” type wall has an average height of 10 +/- feet above the landside ground surface and is about 4,040 feet long. The “I” type wall has an average height of about 9 +/- feet above the landside ground surface and is about 8,060 feet long. Construction of the floodwall began in 1947 and was completed in 1951.
Floodwall is constructed where clearance would be too restricted for levee construction. The floodwall is constructed of reinforced concrete with a steel sheet pile cutoff. There are two specific types of concrete floodwall, I-Wall and T-Wall. Each type has several different designs to accommodate different conditions. Concrete floodwall is constructed on-top “sheet pilings” (pictured at left). T-Wall sheet piling was driven through the soil down to bedrock. The “T” type wall has an average height of 10 +/- feet above the landside ground surface and is about 4,040 feet long. The “I” type wall has an average height of about 9 +/- feet above the landside ground surface and is about 8,060 feet long. Construction of the floodwall began in 1947 and was completed in 1951.
I-Wall has 3 different design types and T-Wall, 7 design types. Floodwall is constructed as free standing panels/monoliths approximately 25 feet in length.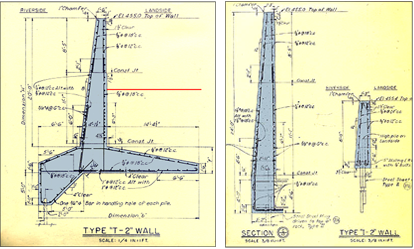
There are 525 panel sections that make up the entire length of the floodwall. The redline (left) indicates the approximate ground surface on the landside. There is about 10,800 linear feet of exposed expansion joints throughout the length of the floodwall.
The concrete wall was poured as a reinforced cap over interlocking steel sheet piling. Sheet pilings provide two critical functions in the floodwall design; they support the concrete cap that rises to an average height of 10 feet above landside ground surface, and to block seepage from the river to the landside. It is critical that the soil does not become over saturated during an event. Once saturated, the soils supporting a wall can quickly begin sliding, causing a collapse.
In order to control saturation, a complex network of wall drains was installed, landside, at the base of the wall. The wall drain is a perforated piping system designed to intercept seepage and channel it to pumping stations. The wall drain system extends for more than 2 miles, parallel to the floodwall, at its base.
Wall “Type” Identification: Markings on the pilasters identify the wall design type. Three vertical grooves indicate “T-Wall”, and two grooves indicate “I-Wall (see drawing at right).

Flood Operations Center
826 Hillside Road
Sunbury, Pennsylvania 17801
All contents © 2015 Sunbury Municipal Authority | site design: BLH Media